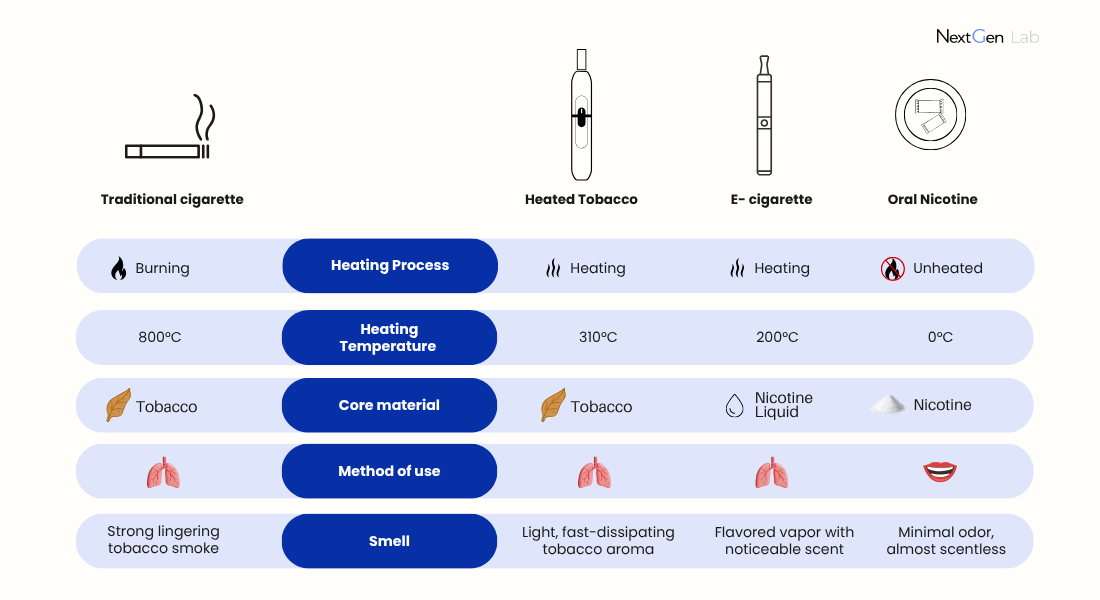
Combustion is the primary source of harmful chemicals in traditional cigarettes. Burning tobacco at 800°C generates thousands of compounds, including tar and over a hundred harmful or potentially harmful constituents.
HNB and e-cigarettes differ fundamentally in heating mechanisms:
- HNB heats real tobacco at 310°C, avoiding combustion and therefore reducing combustion byproducts.
- E-cigarette vaporize nicotine liquid at around 200°C, with no actual tobacco.
- Oral Nicotine requires no heating or combustion, delivering nicotine via oral absorption.
Higher temperatures drive stronger tobacco pyrolysis and chemical emissions:
- Cigarette: 800°C (highest exposure)
- HNB: 310°C (moderate thermal decomposition)
- E-cigarette: 200°C (low thermal decomposition)
- Oral Nicotine: 0°C (no thermal decomposition)
This creates a “risk gradient,” where lower heating temperatures generally correlate with reduced tar, carcinogens, and particulate matter exposure.
- Cigarette & HNB use tobacco, catering to traditional taste preferences.
- E-cigarette use nicotine liquid, offering diverse flavor profiles.
- Oral Nicotine rely on powdered nicotine, prioritizing convenience and discretion.
The material difference influences user perception of taste, risk, and suitability for different scenarios.
As global smoke-free policies tighten, “usage flexibility” has become a major competitive differentiator.
- Cigarette produce strong, lingering odor.
- HNB generates light, fast-dissipating aroma.
- E-cigarette produce flavored vapor with noticeable scent.
- Oral Nicotine is nearly odorless.
Odor reduction is a key driver behind female adoption and socially sensitive user groups.
Nicotine technologies are shifting from combustion to heating and ultimately to non-heating formats, reshaping user experience, risk profiles, and regulatory frameworks. Brands and industry stakeholders must leverage these differences to build clearer product positioning and more informed market strategies.
