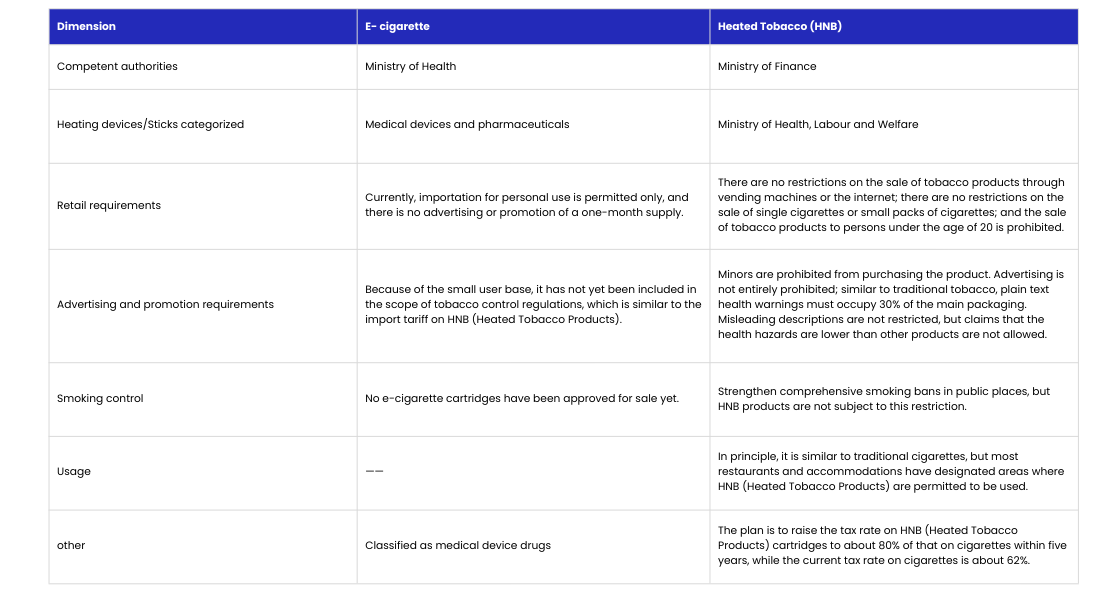
In Japan, heated tobacco products (HNB) are primarily regulated by the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. HNB is considered a tobacco product and is called heated cigarette (たばこ). The Tobacco Business Act regulates the use of heated cigarettes. The Tobacco Tax Law was revised in 2008, establishing a new category of "heated cigarettes." Currently, there are no specific ingredient restrictions for this type of tobacco product, but there are restrictions on warning labels, which are currently plain text. Cigarettes must display nicotine and tar content on the packaging. HNB sales in Japan require a license from the Ministry of Finance. Japan revised the Health Promotion Law, strengthening comprehensive smoking bans in public places, but HNB products are not subject to these restrictions. In terms of sales channels, online, vending machines, convenience stores, and specialty stores are permitted. The law does not prohibit any form of tobacco advertising, promotion, or sponsorship. Heated tobacco products in Japan must display nicotine and tar content on the packaging. Battery-powered devices also require PSE certification. The following are the regulatory differences between HNB and e-cigarettes.
Although retail access is flexible, Japan enforces strict requirements for HNB distribution:
- Mandatory warnings on “impact on others,” “impact on users,” and “minors prohibited”
- At least 50% of the main display area must be covered by warnings
- Nicotine/tar emission testing, PSE certification, and METI device registration required
- HNB taxation uses a complex cigarette-equivalent conversion formula
This model—commercial freedom paired with strict compliance—supports rapid adoption while maintaining regulatory accountability.
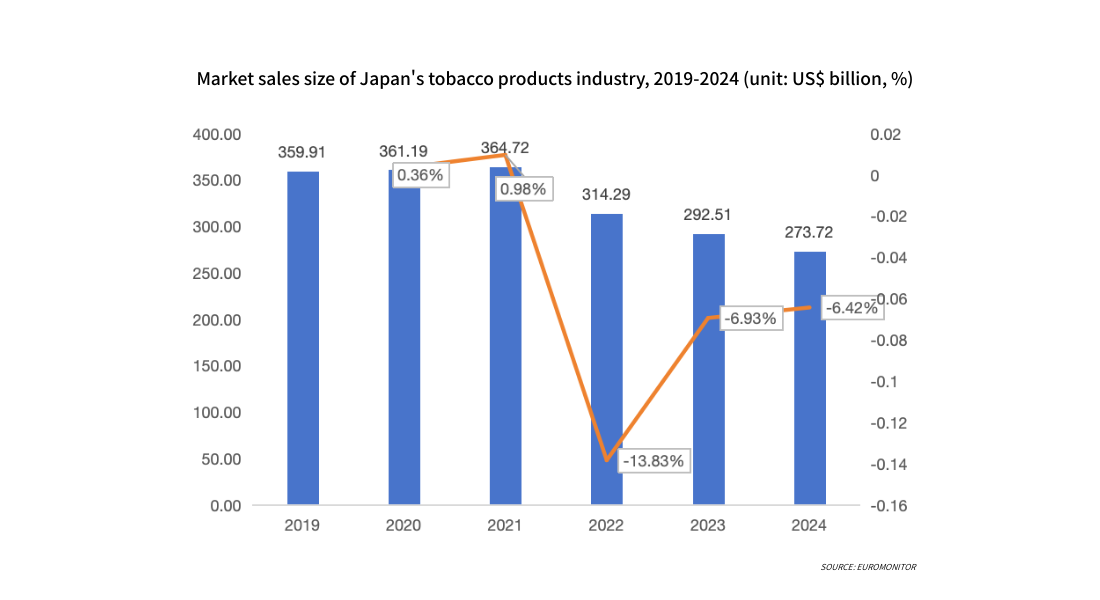
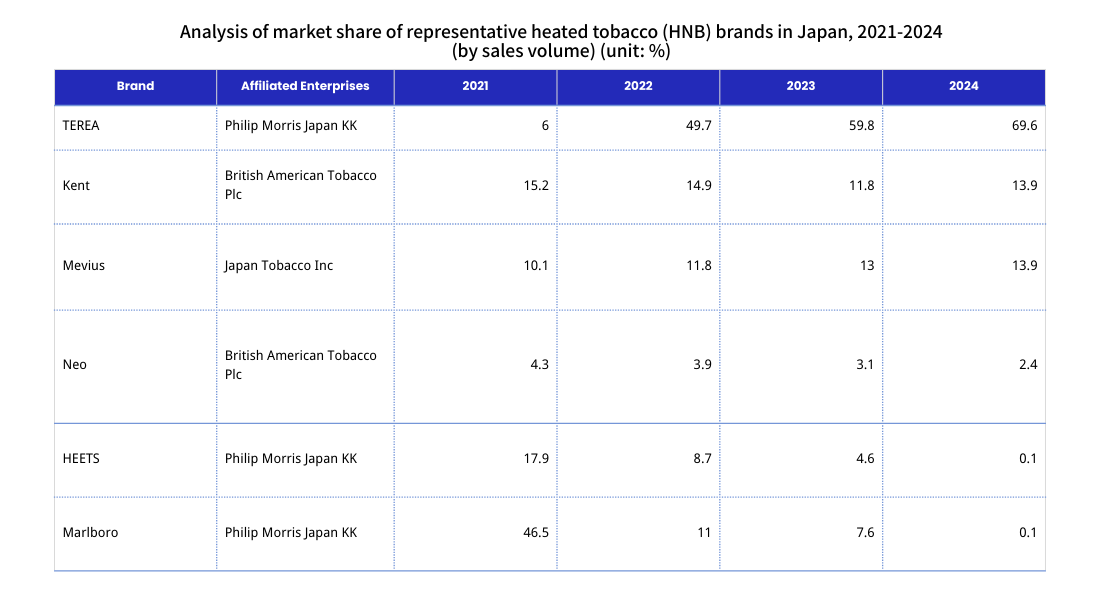
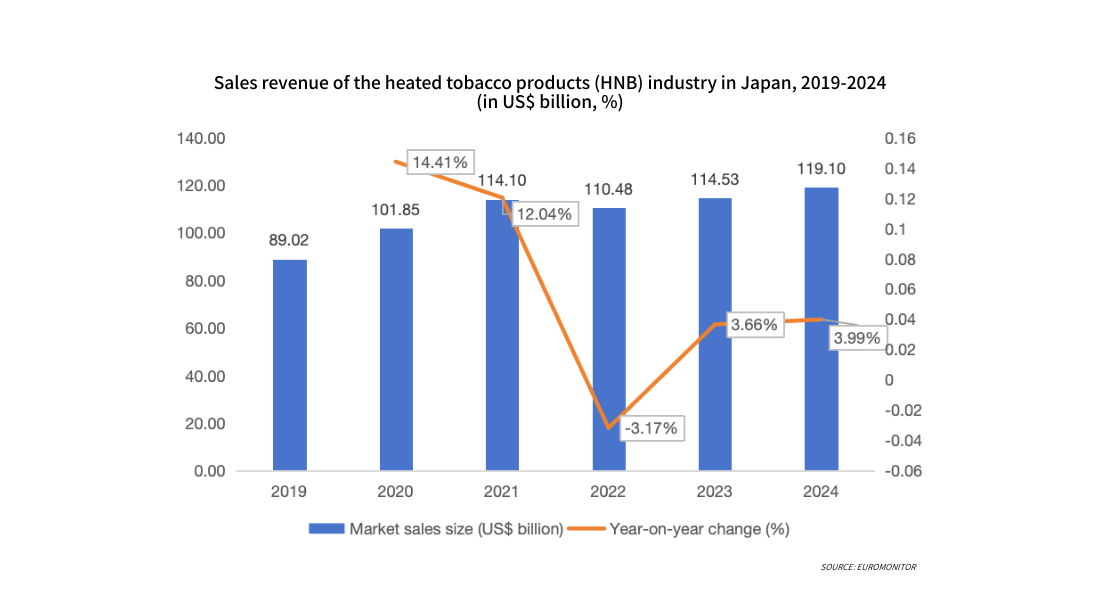
From 2019 to 2024, the structure of the Japanese tobacco product market underwent significant adjustments, with the proportion of traditional cigarettes continuously declining and heated tobacco products (HNB) becoming the main substitute. Driven by policy support (such as Japan's Health Promotion Law allowing its indoor use in specific locations) and product positioning, HNB's market share has steadily increased, gradually approaching the level of traditional cigarettes. Overall, HNB is becoming a significant force driving the evolution of the Japanese tobacco market structure. In 2024, heated tobacco products accounted for 43.51% of all tobacco products in Japan.

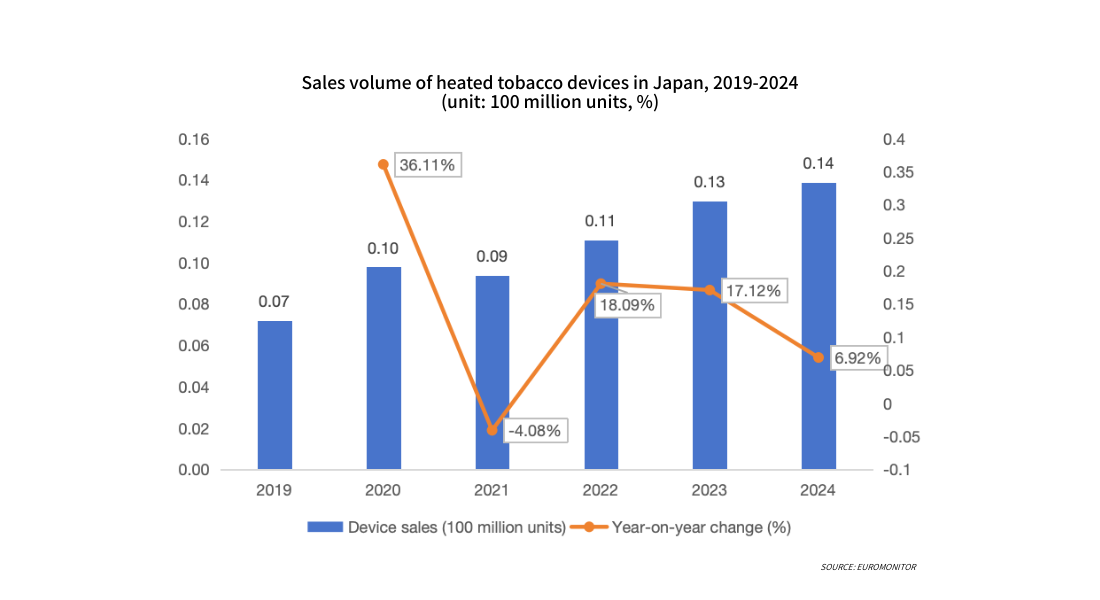
From 2019 to 2024, sales of heated tobacco devices in Japan showed an overall upward trend. Early growth was primarily driven by product iterations and promotions, while the mid-term saw slight fluctuations due to market adjustments. In 2024, device sales reached approximately 14 million units, with the growth rate stabilizing. Rising penetration rates coupled with a slowdown in new user acquisition meant that sales growth stemmed more from replacement demand from existing users than from the expansion of new users, indicating that the market has gradually entered an operational phase centered on repeat purchases of tobacco cartridges.
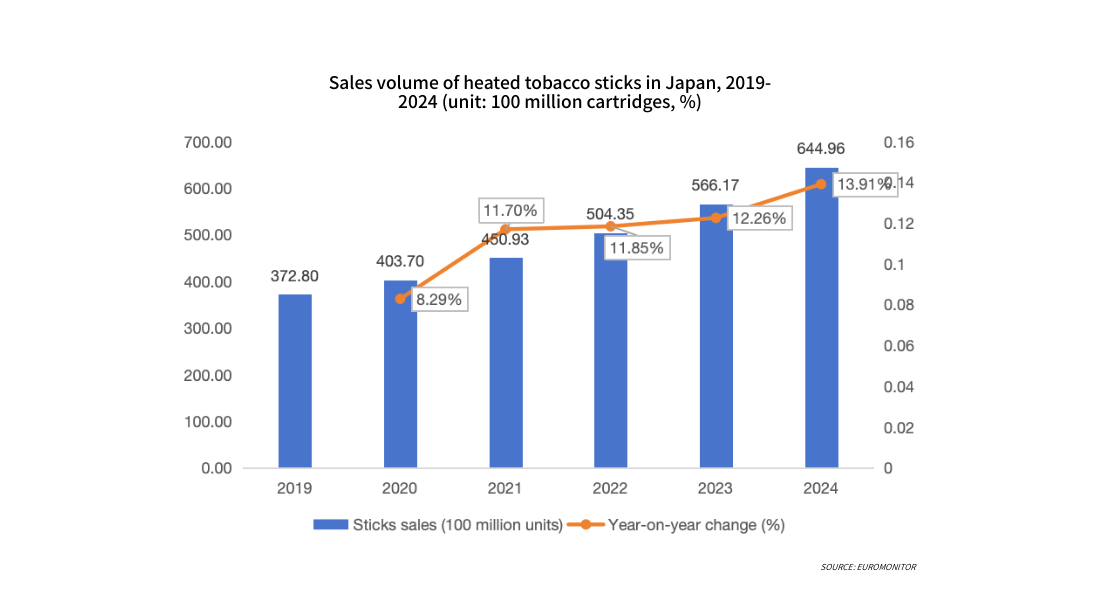
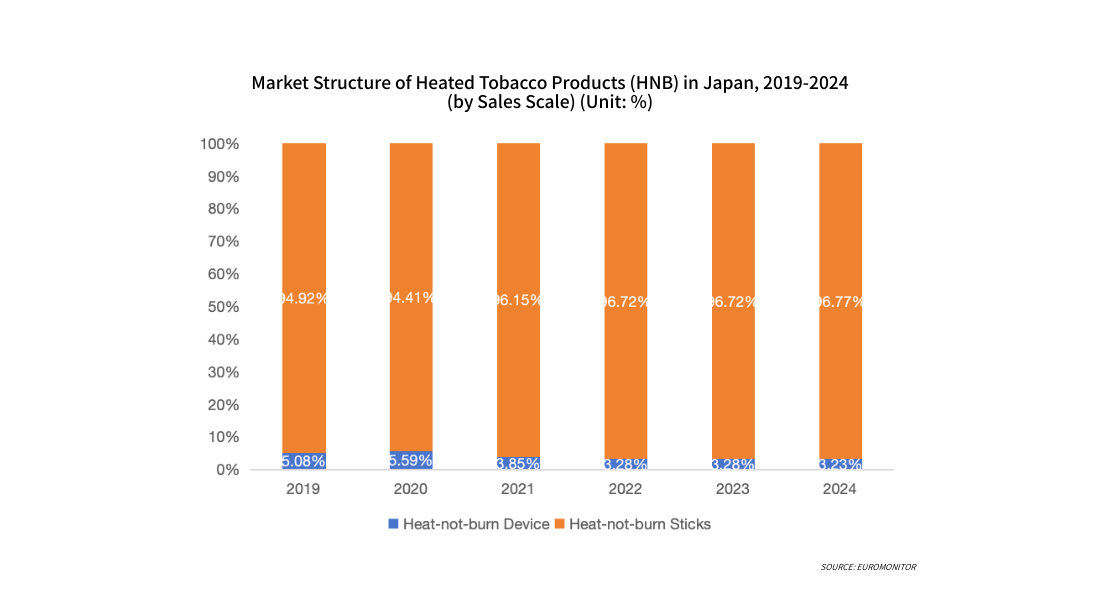
From 2019 to 2024, sales of heated tobacco product (HNB) cartridges in Japan continued to grow, with the average annual growth rate gradually increasing. Total sales in 2024 approached 65 billion cartridges, an increase of over 13% compared to 2023. This trend indicates that with deepening market education and enhanced user loyalty, repeat purchases of HNB cartridges have become the main driver of industry growth. In contrast to the decline in traditional cigarette sales, this further solidifies the proportion and importance of HNB in overall tobacco consumption.